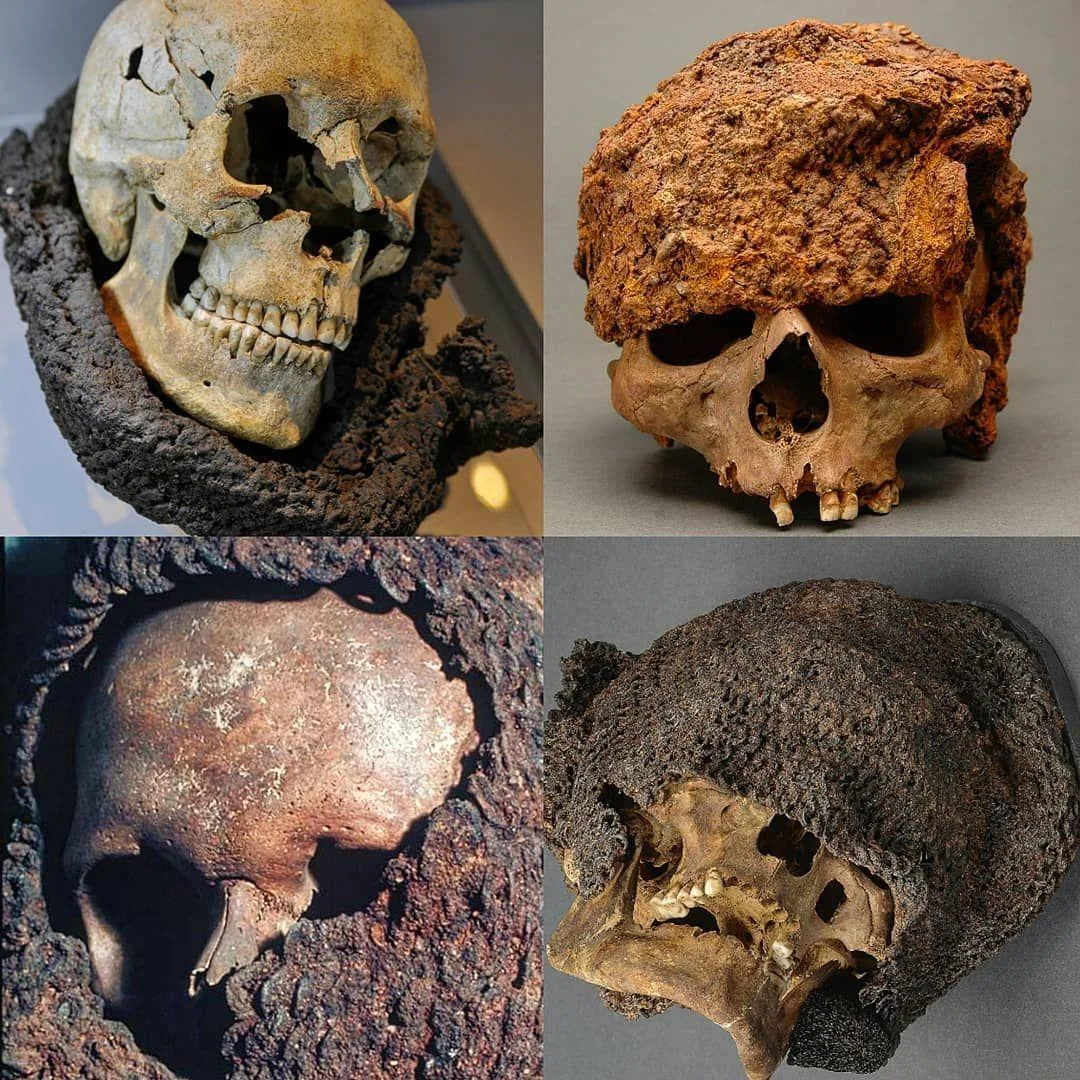
The discovery of medieval chainmail skulls in Visby mass graves has provided historians with a unique and detailed insight into medieval combat and armor. These archaeological findings shed light on the harsh realities of warfare during that period, offering a glimpse into the protective measures taken by soldiers.
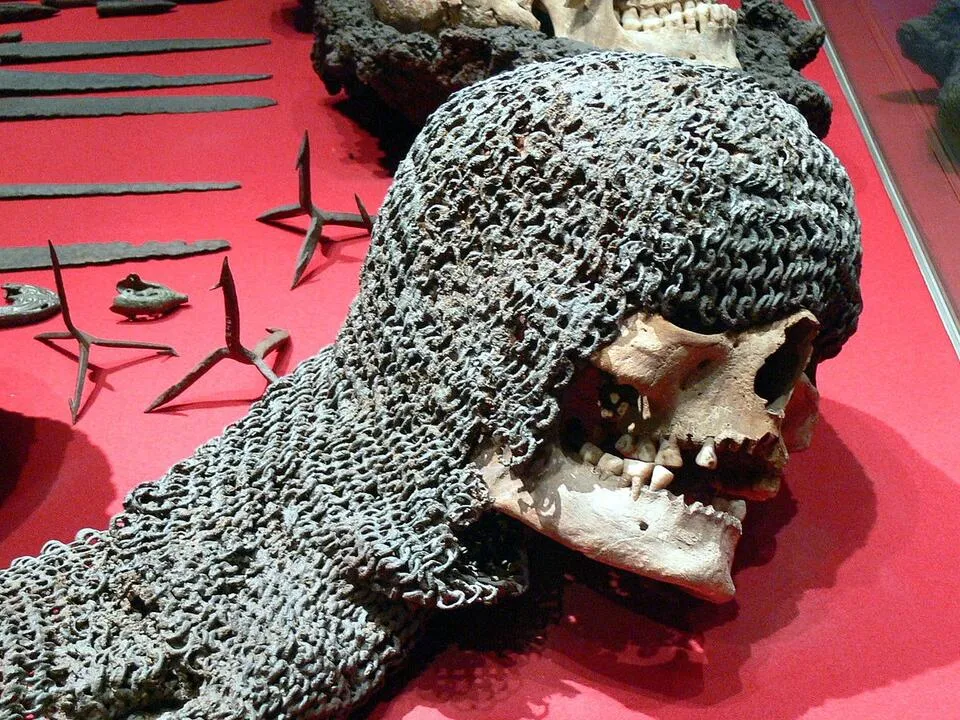
Chainmail, a type of armor made of interlinked metal rings, was a crucial element in medieval military attire. The presence of chainmail on the skulls found in Visby suggests that these individuals were equipped with protective headgear, emphasizing the importance of safeguarding the head in battle.
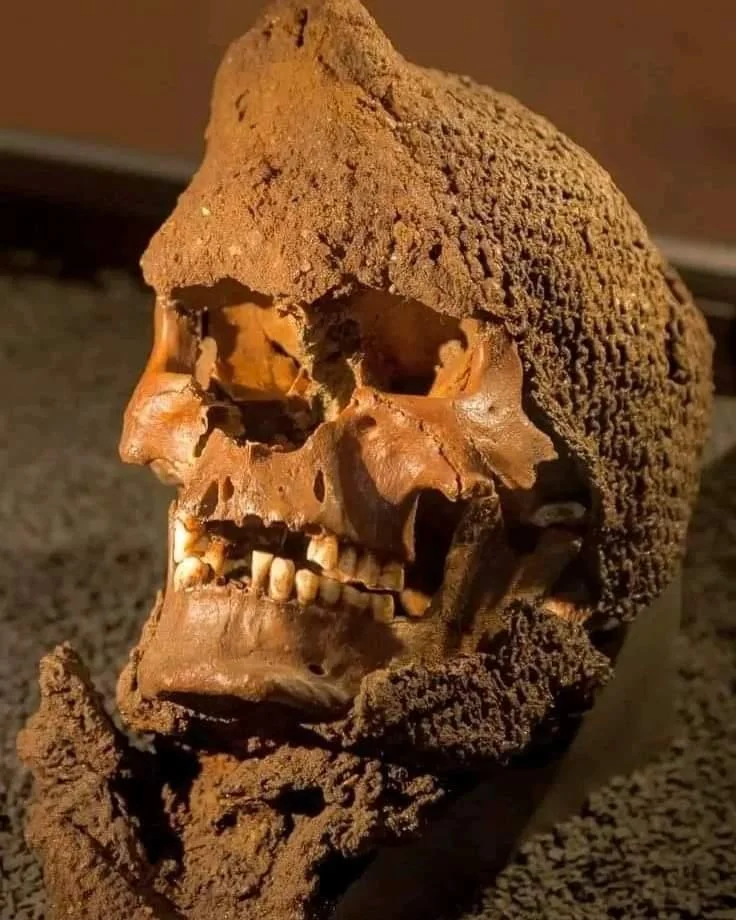

The condition and distribution of the chainmail on the skulls can reveal valuable information about the nature of combat during the medieval era. Analysis of the chainmail may indicate patterns of wear and damage, providing clues about the types of weapons used and the intensity of the battles in which these individuals were involved.
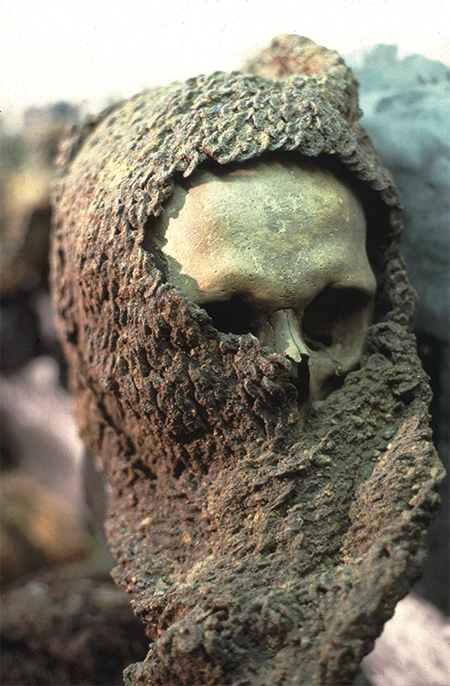

Furthermore, studying the placement and design of the chainmail on the skulls can offer insights into the craftsmanship and technology of medieval armor production. This knowledge contributes to a deeper understanding of the socio-economic aspects of warfare, including the resources and skills required to manufacture such protective gear.
The Visby mass graves, with their preserved artifacts and skeletal remains, serve as a tangible link to the past, allowing historians to reconstruct the narratives of medieval conflicts. By examining these chainmail-adorned skulls, researchers can piece together the stories of individual warriors and gain a more comprehensive understanding of the challenges and strategies employed in medieval warfare.






